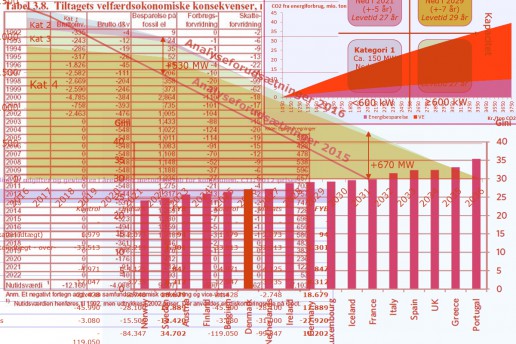
Theoretical glasses
Introduction: Theoretical glasses
A theory can be understood as a particular type of glasses, which make it possible to see certain things while other things disappear.
Institutions
We often talk about different kinds of institutions, such as children’s institutions, educational institutions, prison institutions or more generally, public institutions.
Systems thinking
Among ecological economists, it is very common to use the word system. According to the system theorist, Donella Meadows, a system consists of a number of connected and interacting elements that are organised in such a way that they achieve something specific.
Tools of persuasion
In this section, we attempt to describe a feature of the economic measures and models that has not been the subject to much research - not in mainstream economics or ecological economics.
The circular economy
Introduction: The circular economy
In a time of increased consumption of energy and resources, it has become commonplace to talk about a so-called circular economy, where energy comes…
Circular thinking
In a time of increased consumption of energy and resources, it has become commonplace to talk about a so-called circular economy, where energy comes…
Product chains
Circular economy is mainly concerned with how so-called product chains can be transitioned so they create more value with fewer resources and less…
The circular economy is not the same as ecological economics
It is our impression that similarities are often made between circular economy and ecological economics. However, this is a mistake as the two are…
Sustainable transitions
Introduction: Sustainable transitions
As the environmental consequences of increasing economic activities have become increasingly alarming, the need for a sustainable transition has also…
Theories of sustainable transition
Over the last 15 years, political interest in a sustainable transition has created the foundation for the establishment of a new independent research…
Cities as transition arenas
Traditionally, energy, transport and water systems have primarily been analysed as nationally delimited systems, whereas, for example, cities or…
Control and regulation
Introduction: Control and regulation
In the themes on energy, metabolism and growth, the focus is on environmental problems in an overall perspective: changing the energy basis in a…
Specific environmental problems
Specific environmental problems emerge in many different ways. A classic problem is that an important resource becomes depleted. As a Danish example,…
The problem of side-effects and third parties
Production and consumption involve both the use of resources and the emission of waste materials, which may cause two kinds of problems: First,…
Property rights and commons
The classification of the different types of goods is based on purely practical assessments of their characteristics: Is it practically possible to…
Markets and environmental regulation
There is no direct connection between the way in which property rights for resources are organised and the way in which the products that are…
Political decisions
Introduction: Political decisions
While in the themes on driving forces and distribution the focus is mostly on conflicts over distribution in relation to the environment in a very…
Socio-economic analyses in practice
Socio-economic analysis is a tool that is often used in connection with establishing political priorities for major societal investments.
Alternatives to cost-benefit analysis – an example
When discussing major construction projects, such as motorways, wind farms or bicycle infrastructure, it has gradually become routine to include…
Ecological economists’ view on value and prices
Socio-economic analyses such as CBA require a common unit of measurement in the form of money. When the advantages and disadvantages are put into…
View on nature and ethics
Introduction: View on nature and ethics
The term, nature, plays an important role in the understanding of sustainability. The way we perceive nature influences how we treat the different…
Nature and ecophilosophy
At first glance, the word nature may not seem very complicated. Nature; it is the forests, mountains, rivers, animals and plants. However, if you…
Nature – in the service of humans
There are many ways of defining nature, but the view of nature as a resource has gradually become widespread. Here nature is regarded as a supplier…
Environmental ethics
In this section, we introduce some important concepts in environmental ethics. These concepts function as tools for discussing various environmental…
Driving forces and distribution
Introduction: Driving forces and distribution
In the theme on the relationship between growth and the environment, it is argued that there are environmental limits to growth in living standards.
The growth engine
Since the start of industrialisation and especially during the post-WW2 period, we who live in the rich countries have been able to increase our…
Trade and globalisation
The idea that free trade is good can be seen as one of the ideas that support the growth engine. However, the idea is challenged when adopting an…
Distribution of use values in a society
As previously mentioned in the theme on growth, ecological economics supports the idea that a society produces a ‘real cake’ during the course of a…
Growth and the environment
Introduction: Growth and the environment
Economic growth is a central theme in economic thinking and it is usually presented as a social good - a necessity for social development.
Biophysical limits to growth
One of the consequences of the biophysical perspective on the economy is the emphasis on limits to growth. In the biophysical perspective, the Earth…
Production result – the ’real cake’
According to ecological economics, there is no doubt that there are limits to growth in biophysical terms. But does this also mean that there are…
The growth dilemma
Despite various criticisms, it is clear that economic growth, measured as GDP growth, is still the key objective of economic policy.
The biophysical perspective
Introduction: The biophysical perspective
In this theme, the economy is presented as a so-called metabolic organism, i.e an organism with a metabolism. This focuses on the economy in a biophysical perspective, which makes an important contribution to the understanding of the economy and economic theory.
A metabolic organism
The word, metabolism, stems from the Old Greek word for change or transition and refers to the transformation of materials and energy.
Measuring the economy’s metabolism
In order to contribute to the sustainable transition of the economy, politicians and other actors need to be aware of how the metabolic process of the economy is going and how different policies affect it.
The energy basis
Introduction: The energy basis
Energy combined with humanity’s ability to exploit its different forms is an important key to understanding the economic development of society.
Humanity’s energy history
In this section, we look at how people have gradually learned to utilise a greater number of energy sources, which has been an important factor in…
The importance of the energy base
One of the important differences between ecological economics and mainstream economics is the interpretation of the role of energy in overall…
The current challenge
The analysis of human history from an energy perspective makes it possible to understand the nature of the most fundamental current challenge: